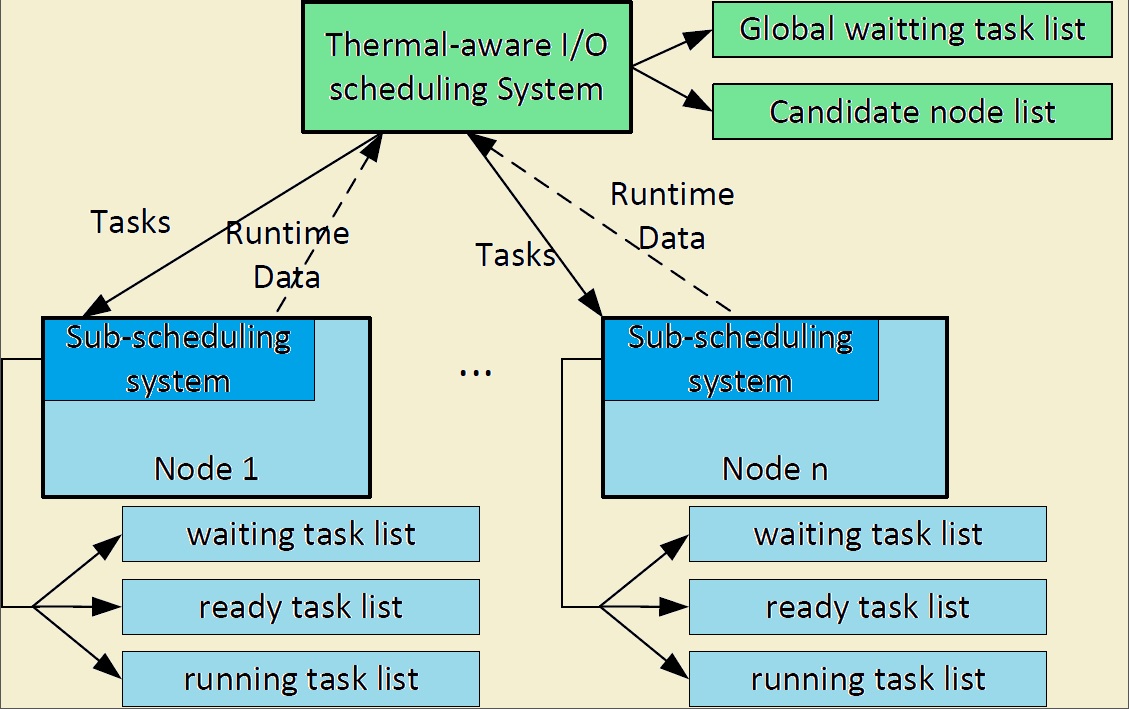
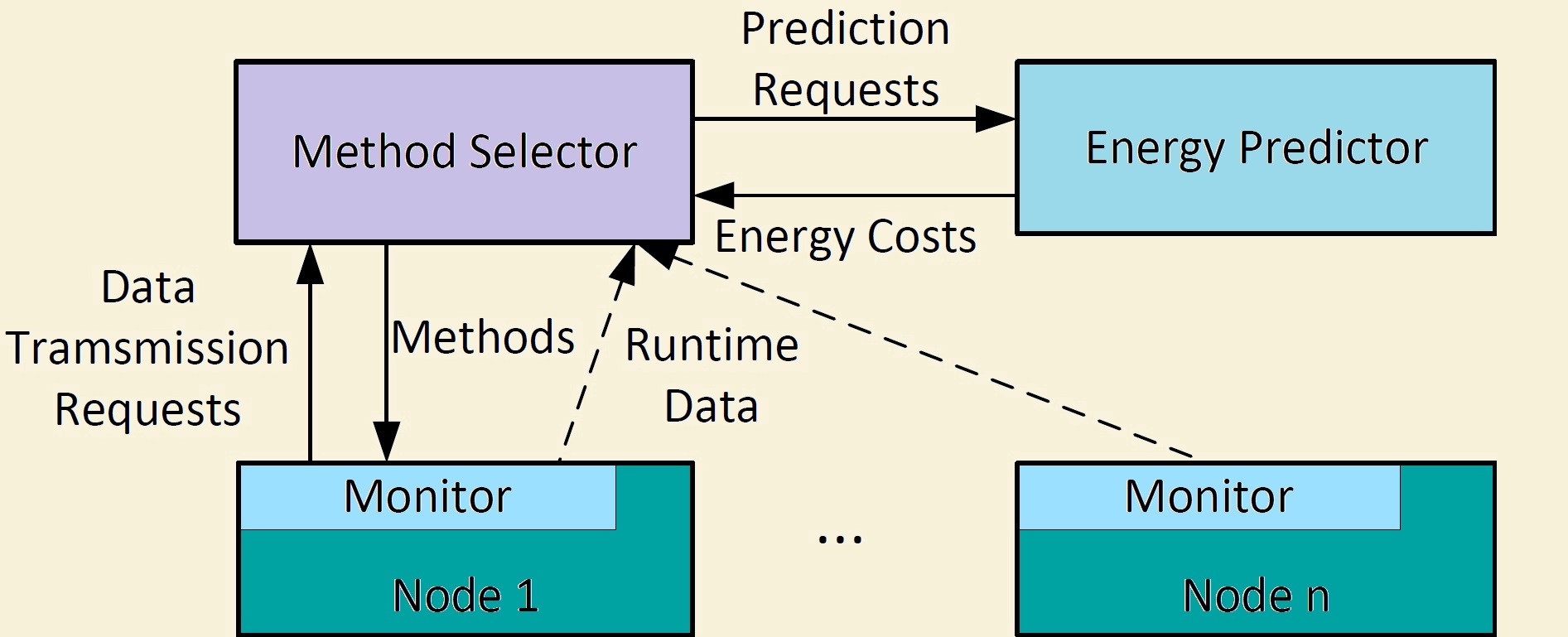
Disks have not been paid fully attention in their impacts on outlet temperatures of data nodes.
In modern data centers, Teradata equipments could support more than 100 disks in a single data node. We expect large affect from the disks' temperature.
We proposed a thermal modeling approach to estimate temperatures of CPUs and disks (including hard drives and solid state disks).
This approach can be applied to investigate thermal behaviours of storage systems under various utilizations patterns.
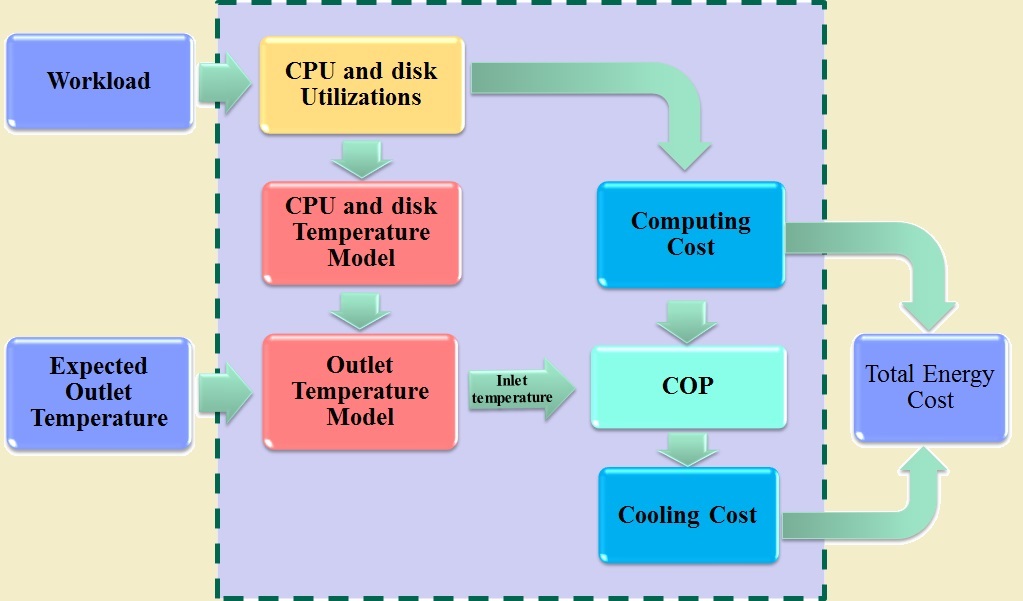
With the thermal modeling approach, outlet temperatures of data nodes can be estimated under particular workloads without deploying temperature sensors in storage systems.
In addition, differences between inlet and outlet temperatures of data nodes can be modeled based on CPU and disk temperatures.
Combining these models enables administrators to set up an appropriate inlet temperature of storage systems, which protects computing facilities from working in high temperature.
Moreover, the cooling costs of storage systems can be calculated by using the proposed thermal model and the COP (Coefficient of Performance) model.
Publications:
[1] X.-F. Jiang, M. I. Alghamdi, J. Zhang, M. Al Assaf, X.-J. Ruan, T. Muzaffar, and X. Qin,
"Thermal Modeling and Analysis of Storage Systems", Proc. the 31th IEEE International Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC), 1-3 Dec. 2012.
(Acceptance Rate: 27.8%, 32/115)
[2] X.-F. Jiang, M. M. Al Assaf, J. Zhang, M. I. Alghamdi, X.-J. Ruan, T. Muzaffar, and X. Qin,
"Thermal modeling of hybrid storage clusters", Journal of Signal Processing Systems, 2013.